Video Resolution – The Ultimate Guide to Display Resolution for Broadcasters
“Resolution” is a term that is thrown around a lot in the video streaming world. Consumers often associate “high-resolution” or “high-definition” with stellar video quality, and in a sense, they are right.
However, video resolution is more than that. It is actually an important measurement in online broadcasting that can be manipulated to optimize the viewers’ experience.
In this post, we’re going to discuss everything you need to know about video resolution and related technology. We’ll start by defining video resolution and two similar measures before we take a close look at common video resolutions. We will also compare SD vs. HD and describe the importance of each.
To wrap things up, we will talk about how to change a video resolution and take a look at some suggested encoder settings to yield the best results.
Table of Contents:
- What is Video Resolution?
- Measurements Related to Video Resolution
- Technology and AI Trends in 2024-2025
- Emerging Display Technologies and Their Impact
- Common Video Resolutions
- HD vs. SD
- Resolution vs. Quality
- What is the Best Video Resolution?
- Video Resolution Use Case Matrix (2025)
- How to Check Video Resolution
- Multi-Bitrate Streaming: Different Qualities for Different Viewers
- YouTube Video Resolution and YouTube Video Dimensions
- How to Change a Video’s Display Resolution
- FAQs
- Conlclusion
What is Video Resolution?
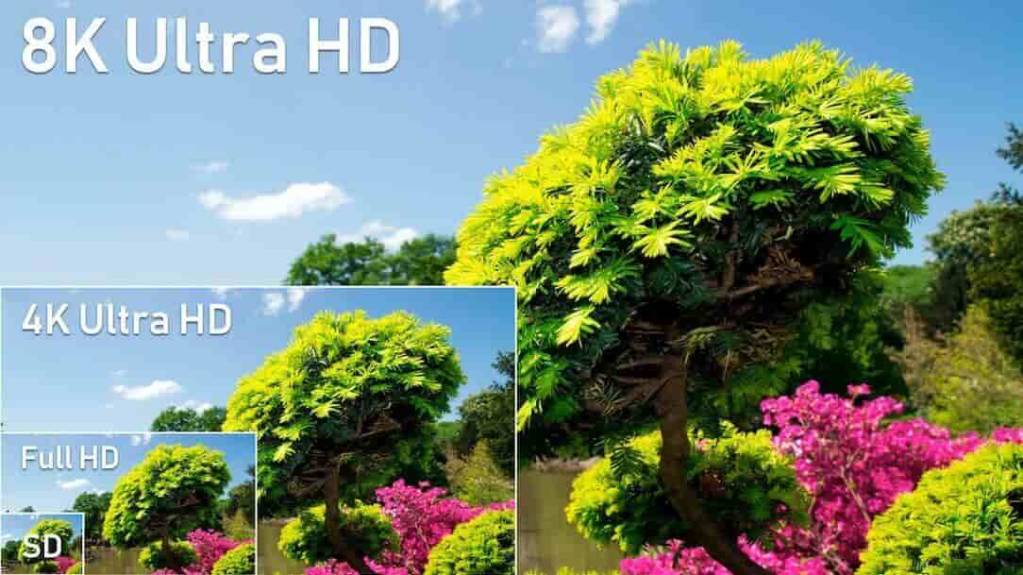

Video resolution is the measurement of a video’s width by height in pixels. For example, a video with a 1920 × 1080 aspect ratio would measure 1920 pixels along the bottom and 1080 pixels in height.
Video resolution depends on a few things, including encoder settings and the capabilities of the camera that you are recording with. Even if your camera is capable of capturing high-resolution content, you may have to experiment with the camera settings to figure out what will produce the best results.
Sometimes, video resolution is referred to by just the height of the video. For example, the 1920 x 1080 resolution can be shortened to 1080i or 1080p. In these abbreviations, “i” stands for “interlaced,” and “p” stands for “progressive.” These two terms refer to how the pixels are displayed on the screen. Progressive is a more fluid image, whereas interlaced is more “pixelated.”
Using resolution to describe the width and height of a video player is called spatial resolution. Spatial resolution is the most common type of resolution in video streaming, but there is also the concept of “temporal resolution.”
Temporal resolution describes the frame rate or the number of frames displayed per second.
Measurements Related to Video Resolution
There are two other measurements that we should discuss before digging further into video resolution: video aspect ratio and video bitrate. Let’s take a look at each of these measurements.
Video Aspect Ratio

Video aspect ratio is the width-to-height ratio of a video. This number is generated by simplifying the ratio of the video resolution.
For example, a video with a 1920 x 1080 resolution would have an aspect ratio of 1920:1080. This figure is simplified to 16:9 by reducing each side by the greatest common multiple. In this case, it is 120.
The most common video aspect ratio is 16:9. This is used for most video players on both modern televisions and mobile streaming devices. In the past, 4:3 was the standard since it was suitable for the size of older television screens, but this has mostly been phased out.
Some social media platforms use different aspect ratios. For example, 9:16 is the standard for video sharing on TikTok and any platform that uses “Stories.” Instagram had previously only supported streaming with a 1:1 aspect ratio, but this has since become more flexible.
Video Bitrate
Video bitrate, on the other hand, measures how much data is being transmitted over a specific amount of time. In video streaming, bitrate is often measured in the unit “kilobits per second,” or ”kbps.” Bits per second (bps) and megabits per second (Mbps) are also used.
Technology and AI Trends in 2024-2025
AI-powered upscaling
From 2024 to 2025, AI video upscaling has seen major growth. Tools like NVIDIA DLSS, Topaz Video Enhance AI, and Adobe’s AI-driven video tools now help broadcasters increase the perceived video resolution without needing extra bandwidth. These tools are especially useful for live streaming and on-demand content, making lower-resolution footage appear sharper and clearer. This is helpful for anyone wondering how to check video quality or how to know video quality without upgrading their capture setup.
Super resolution via AI
AI-based super resolution helps improve video quality from older or low-resolution sources. Whether you’re restoring archived footage or enhancing mobile captures, AI models can fill in missing detail and reduce blur. For broadcasters needing to check video quality or wondering how to check if a video is 4K, these tools can make a noticeable difference in how the content looks—especially on larger displays.
Smart encoding
Leading video platforms are now using smart AI-enhanced encoders, such as those from Bitmovin and AWS Media Services. These tools analyze content in real time—motion, lighting, detail—and adjust encoder settings for streaming to deliver the best resolution at the lowest possible bitrate. This is essential for adaptive bitrate streaming and maintaining a balance between video quality vs resolution. Broadcasters looking for a reliable video quality checker online or video resolution checker can use these systems to automate optimization across devices and bandwidth levels.
Emerging Display Technologies and Their Impact
New display technologies are changing how viewers experience video. Devices like 8K TVs and 5K monitors push the need for ultra-high-resolution content. Foldable screens and XR headsets add another layer of complexity by demanding flexible, high-quality visuals that scale across different screen sizes and shapes. This shift raises important questions like how to check if video is 4K or not, or how to find the resolution of a video before distribution.
With modern displays supporting variable refresh rate (VRR), resolution now works closely with frame rate. Smooth playback is just as important as clarity. High resolution paired with steady frame rates improves visual quality, which you can evaluate with a video quality tester or check video quality online tools. This makes understanding video quality metrics and video quality standards more important than ever.
Codec Comparison: H.264, H.265, AV1, and H.266/VVC
As video resolutions like 4K and 8K become more common, choosing the right codec is essential for efficient delivery. Older formats like H.264 are still widely used and work well for HD streaming, but they struggle with higher resolutions. H.265 (HEVC) improves compression for 4K video, but newer codecs like AV1 and H.266/VVC are designed specifically for ultra-high-definition streaming. These modern formats can deliver stunning video quality at much lower bitrates, which helps reduce bandwidth costs without sacrificing performance.
Understanding codec compatibility is crucial when you want to check resolution of video files or find the resolution of a video. These tools also play a key role in how to check the quality of a video or compare 1080p vs 4K in real-world conditions.
Common Video Resolutions
Understanding and knowing the most common video resolutions will help you select the best video quality for your requirements. Below are the standard video resolutions:
- SD (Standard Definition): 480p, 4:3 aspect ratio, 640 x 480 pixels. Suitable for basic viewing. Often used in older content and broadcasts.
- HD (High Definition): 720p, 16:9 aspect ratio, 1280 x 720 pixels. Offers better clarity. Ideal for general viewing on smaller screens.
- Full HD (FHD): 1080p, 16:9 aspect ratio, 1920 x 1080 pixels. Common for most modern content. It provides excellent detail and clarity.
- QHD (Quad HD): 1440p, 16:9 aspect ratio, 2560 x 1440 pixels. Offers higher resolution than Full HD. Great for high-quality video and gaming.
- 2K Video: 1080p, 1:1.77 aspect ratio, 2048 x 1080 pixels. Slightly wider than Full HD. Used in some professional formats.
- 4K Video or Ultra HD (UHD): 2160p, 1:1.9 aspect ratio, 3840 x 2160 pixels. Provides ultra-high definition. Perfect for large screens and high-end productions.
- 8K Video or Full Ultra HD: 4320p, 16:9 aspect ratio, 7680 x 4320 pixels. The highest current resolution. It delivers unparalleled detail and clarity for future-proofing content.
Video Resolution Comparison Chart (2025)
Here’s a handy, easy-to-read comparison chart that includes standard, vertical, and ultra-wide resolutions. This version is optimized for 2025 broadcasting and streaming use cases, including vertical content (TikTok, Reels, Shorts) and ultra-wide formats used in gaming or cinematic production.
| Resolution Name | Pixel Count | Aspect Ratio | Use Case | Recommended Bitrate (Streaming) |
| SD (480p) | 720 x 480 | 4:3 or 16:9 | Legacy systems, low-bandwidth live streaming | 1–2 Mbps |
| HD (720p) | 1280 x 720 | 16:9 | Basic live streaming, mobile-friendly | 2.5–5 Mbps |
| Full HD (1080p) | 1920 x 1080 | 16:9 | YouTube, webinars, general broadcasting | 5–8 Mbps |
| Vertical HD | 1080 x 1920 | 9:16 | TikTok, Reels, YouTube Shorts | 2.5–6 Mbps |
| 2K Cinema | 2048 x 1080 | ~17:9 | Film and cinematic production | 8–12 Mbps |
| Quad HD (1440p) | 2560 x 1440 | 16:9 | Gaming streams, mid-range YouTube content | 10–16 Mbps |
| 4K UHD | 3840 x 2160 | 16:9 | High-end streaming, OTT platforms | 16–30 Mbps |
| Vertical 4K | 2160 x 3840 | 9:16 | Vertical 4K social video, signage | 16–30 Mbps |
| 5K | 5120 x 2880 | 16:9 | Creative work, ultra-clear displays | 25–40 Mbps |
| Ultra-Wide QHD | 3440 x 1440 | 21:9 | Gaming, simulators, immersive experiences | 12–18 Mbps |
| Ultra-Wide 4K | 5120 x 2160 | 21:9 | Cinematic content, premium video experiences | 25–45 Mbps |
| 8K UHD | 7680 x 4320 | 16:9 | Next-gen OTT, future-proof archives | 50–100+ Mbps |
HD vs. SD
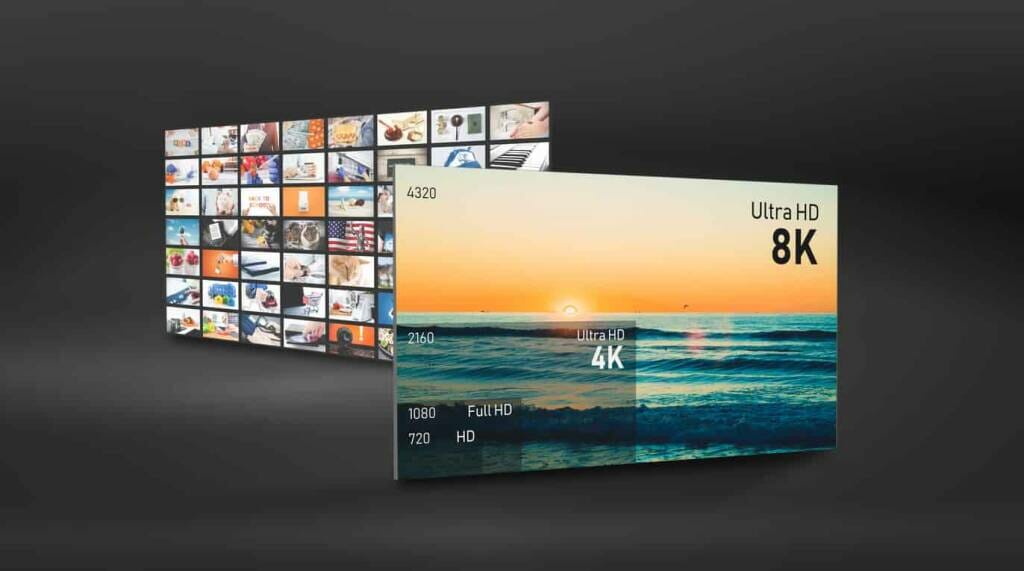

Over the past decades, we’ve witnessed a massive transition from standard definition (SD) to high-definition (HD) streaming. HD streaming (or better) is definitely the norm at this time. Just about any new television will come with HD streaming at the absolute least.
The only thing that is keeping SD hanging on by a limb is bandwidth constraints. Sometimes broadcasters drop to SD to make their streams more suitable for streaming over slower internet or to ration bandwidth allotments.
It is also important to note that SD is more commonly used with older television sets that support streaming with a 4:3 aspect ratio. Since these television sets are rather outdated, standard-definition streaming is inching towards death.
The bottom line is that most modern broadcasters are using HD streaming or better.
Resolution vs. Quality
Many people assume that a higher resolution always means better quality, but that is not always true. Video resolution simply refers to the number of pixels in the image, while quality depends on more factors—especially bitrate. For example, a 1080p video streamed at just 400 kbps will look far worse than a 720p video streamed at 2500 kbps. That’s because bitrate controls how much detail is preserved during compression.
To better measure what viewers actually perceive, tools like video quality metrics (such as VMAF scores) are used. These scores help gauge how good a video looks to the human eye, even when resolutions are the same.
In today’s streaming world, resolution also interacts with frame rate and technologies like variable refresh rate (VRR). A 4K video at 15 fps may feel choppy, while a 1080p stream at 60 fps with VRR can appear smoother and more responsive. That’s why streaming resolution comparison isn’t just about pixel count—frame rate, compression, and encoding quality matter too.
For anyone wondering how to check if video is 4K or not, or how to check quality of video, it helps to understand both resolution and perceptual quality. Use a video quality tester or check video specs to get the full picture. Whether you’re trying to figure out how to find the resolution of a video or deciding on the best resolution for streaming, balancing all these factors is key to high-quality viewing experiences.
What is the Best Video Resolution?
Many broadcasters are left wondering what the best video resolution is, and it is difficult to answer that question. There is not one single “best” video resolution. Different resolutions are suitable in different use cases.
For optimal video quality, you must select the right resolution for your needs. For example, YouTube influencers often use Full HD (1080p) for clear, professional-looking content that looks great on both computers and mobile devices. Streaming services such as Netflix offer 4K Ultra HD (2160p) for their best movies and TV shows, providing incredible detail and the most vibrant colours on larger screens. Furthermore, gaming enthusiasts often prefer QHD (1440p) to balance performance with quality. And HD videos (720p) are perfect for quick uploads and less demanding content.
Each of these HD resolutions caters to specific needs and ensures the best viewing experience.
Video Resolution Use Case Matrix (2025)
Below is a video resolution use case matrix designed to help broadcasters, content creators, and technical teams choose the best resolution for different platforms, devices, and industries in 2025.
This matrix helps answer practical questions like:
- How to know the quality of a video?
- What’s the best resolution for streaming in each scenario?
- How can I check the resolution of a video before uploading?
| Resolution | Platform | Device | Industry | Best For |
| 720p (HD) | YouTube, Zoom | Mobile | Education, Fitness | Low bandwidth, quick loads |
| 1080p (Full HD) | YouTube, Twitch | Mobile, Smart TVs | Broadcast, Fitness | Balanced quality and accessibility |
| Vertical 1080p | TikTok, Reels | Smartphones | Personal, Fitness | Vertical-first mobile content |
| 1440p (QHD) | Twitch, YouTube | Gaming monitors | Gaming, Tutorials | Sharper detail without 4K demands |
| 4K (UHD) | YouTube, OTT (Dacast) | Smart TVs, Desktop | Broadcast, OTT | High-end streaming with AV1 codec |
| Ultra-Wide | Twitch, Cinematic | Curved Displays | Gaming, Film | Immersive, widescreen production |
| 8K | OTT (archive, future) | Smart TVs, VR headsets | High-end Broadcast | Future-proof, ultra-detailed archives |
How to Check Video Resolution
To check video resolution and understand its quality, there are a few simple steps to follow. First, video resolution refers to the number of pixels displayed on the screen, which impacts clarity and detail. Some of the most common resolutions include HD (1280×720), Full HD resolution (1920×1080), and 4K (3840×2160).
To determine a video’s resolution on your computer, right-click the video file and select “Properties” (Windows) or “Get Info” on Mac. Under the “Details” or “More Info” tab, look for the resolution. Typically, this is displayed as width x height, such as 1920×1080.
When using media players such as VLC, you can check the resolution by opening the video and then selecting “Tools”. Then, select “Codec Information”. The “Resolution” field will show the dimensions for HD video and other resolutions.
It’s important to understand the video quality types and differences. HD video resolution (720p) is suitable for basic viewing, but it’s rather dated and most screens and devices can display more. Full HD video (1080p) offers superior clarity for most purposes. The term “1080p” refers to 1080p video resolution. What does 1080p mean? It refers to the video having 1080 horizontal lines of vertical resolution. This provides excellent image resolution.
Knowing how to check video resolution ensures you choose the best video quality for your needs. Whether it’s streaming, editing, or general viewing, knowing and understanding video screen resolution and video sizes helps you select the best video resolution for optimal video quality.
Multi-Bitrate Streaming: Different Qualities for Different Viewers
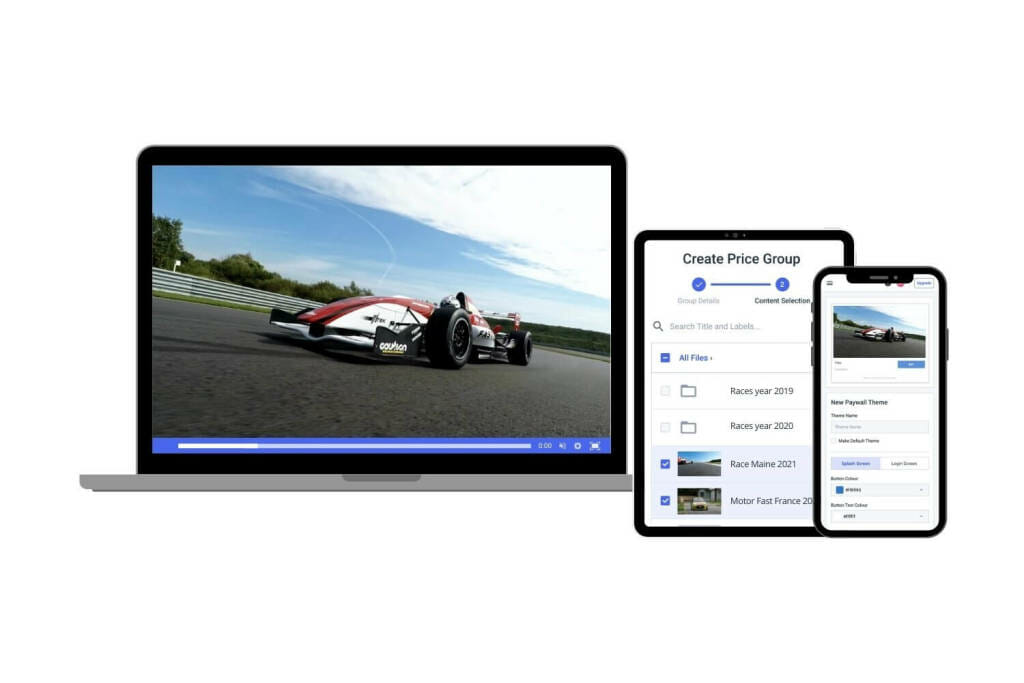
As we mentioned, sometimes streaming at a high resolution is great in theory, but when even a small part of your audience has slow or unreliable internet, this is simply not possible.
Multi-bitrate streaming comes in handy for broadcasters who want to accommodate every viewer in their audience, no matter what sort of internet connection they have. This helps to reduce lagging and buffering, which are two things that can hinder a viewer’s experience.
With multi-bitrate streaming, you can distribute multiple renditions of a video stream that are of different sizes. This accommodates different internet connections by sending the optimal version of the video based on the viewer’s internet speed. That means that viewers with slower internet will be delivered a smaller rendition, and viewers with faster internet will be delivered a larger rendition.
Multi-bitrate streaming paired with an adaptive bitrate video player makes it possible to automate the entire process. This is a more advanced alternative to a more dated setup that requires that viewers manually choose a video resolution.
Not all streaming platforms or broadcasting software offerings support multi-bitrate or adaptive bitrate streaming.
YouTube Video Resolution and YouTube Video Dimensions
When uploading videos to YouTube in 2024, understanding video resolution and dimensions is crucial for achieving the best video quality. YouTube supports various standard video resolutions including HD screen resolution (1280×720), Full HD (1920×1080), and 4K (3840×2160).
For broadcasters, the best settings maximize visual quality while ensuring maximum compatibility across devices. For HD screen resolution, 1280×720 is ideal for basic content. Furthermore, 1920x1080p is perfect for Full HD resolution, which offers crisp, detailed imagery suitable for most viewers. For the absolute best quality, especially for larger screens, 4K resolution at 3840×2160 is the best video quality.
YouTube video dimensions should match the following resolution to avoid black bars, stretching, or other distortions. Common standard video sizes include:
- 720p HD: 1280×720
- 1080p Full HD: 1920×1080
- 4K Ultra HD: 3840×2160
A video resolution chart can help you in selecting the appropriate resolution for different content and devices. For example, the resolution for HD is great for quick uploads and mobile viewing. On the other hand, Full HD and 4K are preferred for high-quality broadcasts and larger screens.
Understanding video screen resolution settings and utilizing the best ones ensures your content looks its best across all platforms and devices.
How to Change a Video’s Display Resolution

There are several reasons why a broadcaster would want to change their video resolution. In a perfect world, every viewer would have lightning-fast wifi and bandwidth would be free. However, that is not the reality.
Broadcasters can change the video’s display resolution by manipulating their video encoder settings. All encoder settings must be properly configured to work with your chosen online video platform.
Bitrate Settings for Resolution
How you configure your bitrate settings plays a major role in the outcome of your video resolution.
You can select one of the following video configurations and ensure your encoder is set up with these exact settings to help prevent streaming issues:
| ULD | LD | SD | HD | FHD | |
| Name | Ultra-Low Definition | Low Definition | Standard Definition | High Definition | Full High Definition |
| Video Bitrate (kbps) | 350 | 350 – 800 | 800 – 1200 | 1200 – 1900 | 1900 – 4500 |
| Resolution Width (px) | 426 | 640 | 854 | 1280 | 1920 |
| Resolution Height (px) | 240 | 360 | 480 | 720 | 1080 |
| H.264 Profile | Main | Main | High | High | High |
Encoder Settings on Dacast
How you configure your encoder settings will determine the quality of your live stream. In some situations, using the wrong setup can cause your stream to malfunction, so you must choose the best encoder settings for your setup.
The following settings are required for live streaming with Dacast, regardless of your selected resolution and bitrate:
| VIDEO CODEC | H.264 (x264 may work) |
| FRAME RATE | 25 or 30 |
| KEYFRAME INTERVAL | 2 secs (or 2x frame rate) |
| SCANNING | Progressive |
| RATE CONTROL | Constant (CBR) |
| AUDIO CODEC | AAC-LC |
| AUDIO BITRATE | 128 kbps |
| AUDIO CHANNELS | 2 (Stereo) |
| AUDIO SAMPLE RATE | 48 kHz (48,000 Hz) |
FAQs
What is the difference between 1080p and 4K?
The main difference is resolution: 1080p (Full HD) has 1920×1080 pixels, while 4K (Ultra HD) has 3840×2160 pixels. 4K offers more detail, especially on larger screens, but resolution alone doesn’t guarantee better quality—bitrate and compression matter too.
Is higher resolution always better?
Higher resolution isn’t always better. While 4K offers more detail, factors like bitrate, compression, and the screen size also affect quality. A high-bitrate 1080p video can look better than a low-bitrate 4K video. Video quality metrics like VMAF scores help assess true visual quality.
What resolution is best for streaming?
The best resolution depends on factors like internet speed, content type, and device. 1080p works well for most streaming, but 4K or even 8K can provide a better experience for large-screen users with high-speed internet. Adaptive streaming, like with Dacast, adjusts resolution based on device and connection.
What is AI upscaling in video?
AI upscaling uses artificial intelligence to improve the resolution of lower-quality videos by adding details and reducing blur. It enhances older or lower-resolution content without needing to re-record in a higher resolution.
Conclusion
As a broadcaster, it is important to understand video resolution. Knowing how to control video bitrate can help you provide a better user experience for your viewers.
Are you looking for an online video platform that supports high-quality streaming? Dacast is a unified streaming solution that is capable of hosting live and on-demand video content. Our platform is fully loaded with the features you need to host, manage, and deliver a professional broadcast.
Some of our top features include white-label streaming, video monetization, easy embedding, all-device streaming, and live-stream recording.
You can try Dacast and all its features with our 14-day free trial.
For exclusive offers and regular tips on live streaming, join our LinkedIn group.
In the meantime, check out the Knowledgebase area on our website. It features a wide variety of documentation on video resolution, multi-bitrate streaming, and Dacast-specific functions. Browse topics or search for keywords. Either way, you’ll find a ton of useful broadcasting information.
 Stream
Stream Connect
Connect Manage
Manage Measure
Measure Events
Events Business
Business Organizations
Organizations Entertainment and Media
Entertainment and Media API
API Tools
Tools Learning Center
Learning Center Support
Support Support Articles
Support Articles