The Broadcasters Guide to HD vs SD Streaming for Live Video
Live video streaming includes a choice between SD and HD, which can significantly shape the viewing experience for your audience. But what exactly is SD quality? SD, or Standard Definition, typically features a resolution of 480p or lower, offering a more basic yet widely compatible viewing experience. While SD streaming may not deliver the sharpest picture, its lower bandwidth requirements make it an appealing option for viewers with slower internet connections.
On the other hand, HD, or high definition, offers a sharper, more vibrant picture, starting at a resolution of 720p. This enhanced clarity leads to a richer viewing experience, improving audience engagement, particularly for content where visual details matter most. HD streaming provides an upgrade in both image quality and viewer satisfaction, making it the preferred choice for many broadcasters.
Understanding the differences between SD and HD streaming is essential for broadcasters. Whether you’re streaming live events, sports, or news, the decision between SD and HD can have a major impact on your audience reach and engagement.
In this article, we’ll dive into the key distinctions between SD streaming vs HD streaming, exploring the pros and cons of each format. We’ll also touch on multi-bitrate streaming and how it can help optimise your broadcasts for different viewer needs.
Table of Contents
- What is Video Resolution?
- HD vs. SD: What’s the Difference?
- Does SD vs. HD Matter for Streaming?
- How to Stream in HD
- How are Resolution and Bitrate Related?
- Detailed Technical Specifications
- Infrastructure and Equipment Requirements
- AI Innovations in HD and SD Streaming
- Conclusion
What is Video Resolution?
Video resolution refers to the number of pixels displayed on a screen, directly affecting the clarity and detail of the video content. It’s typically represented by width x height (e.g., 1280×720), which indicates the number of pixels in each dimension. The higher the resolution, the more detailed and sharper the image appears.
In the streaming context, SD and HD are terms often used to describe video quality. SD resolution usually refers to 480p or 640×480 pixels. Providing a basic viewing experience. SD streaming remains popular due to its lower bandwidth requirements, making it accessible even with slower internet connections. It’s a solid choice for content where high detail isn’t crucial, such as for some news broadcasts or general entertainment.
On the other hand, HD resolution offers a much crisper and clearer image, starting at 720p (1280×720) and going up to 1080p (1920×1080) and beyond. HD streaming is now the standard for most broadcasters, delivering superior image clarity that’s ideal for content where every detail counts, like sports or high-end productions.
Understanding the difference between SD streaming vs HD streaming is essential for broadcasters to meet audience expectations. Whether you’re delivering content in SD or HD, choosing the right resolution helps enhance the viewing experience and ensures your broadcasts are suited to your viewers’ needs.
What is an Aspect Ratio?
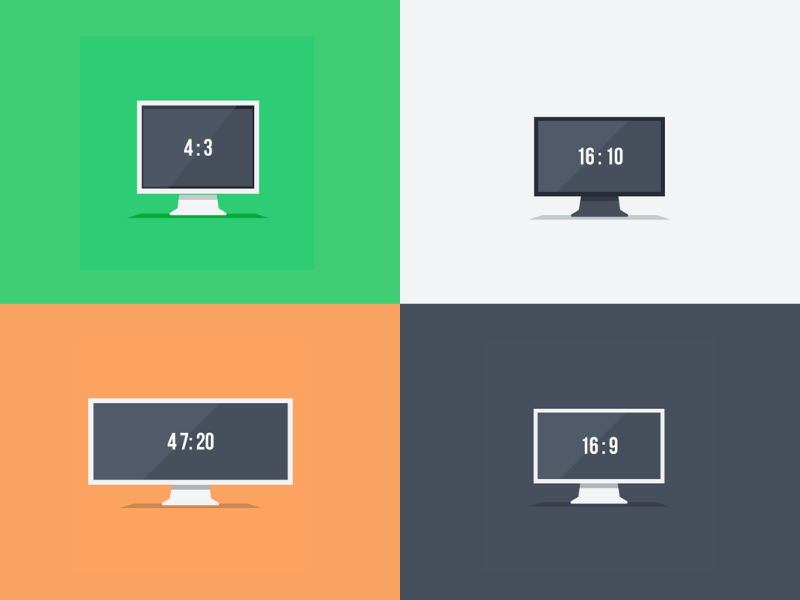


Video aspect ratio is another concept that is important to understand before dissecting SD and HD video streaming.
The aspect ratio describes the width-to-height ratio of a video. This also uses pixels to measure, but the figure is reduced to a simple ratio. For example, a video with 1920 × 1080 resolution has an aspect ratio of 16:9.
The 16:9 aspect ratio has become the standard for most streaming platforms, providing a wide-screen viewing experience. However, other ratios like 1:1 and 4:3 are also common, especially for mobile and older content. The shift from 4:3 to 16:9 happened as widescreen TVs became the norm.
HD vs. SD: What’s the Difference?
The primary difference between HD vs SD streaming lies in the resolution, which directly influences the quality of the video. Let’s break down what each format entails and how it impacts the viewing experience.
What is SD Streaming?
SD streaming refers to Standard Definition streaming, where the video is delivered at a resolution typically around 480p (640×480 pixels). This resolution provides a basic viewing experience, suitable for content where ultra-clear visuals aren’t essential. SD streaming is often the go-to choice when bandwidth usage is a concern, as it requires significantly less data compared to higher resolutions.
For many viewers, particularly those with slower internet connections, SD streaming benefits include accessibility and reliability. It allows for stable, uninterrupted streaming, even in lower-bandwidth environments. SD video quality is still a widely used option for streaming, particularly in regions with limited internet infrastructure or when a lower-quality stream is sufficient.
What is HD Streaming?
HD streaming refers to transmitting video in High Definition, offering a much clearer, more detailed image. HD resolution typically starts at 720p (1280×720) and goes up to 1080p (1920×1080), with 4K streaming now becoming increasingly popular for ultra-high-definition content. HD streaming is ideal for situations where visual clarity is crucial, such as sports broadcasts, live events, and films, where every detail enhances the viewer’s experience.
What is 4K Streaming?
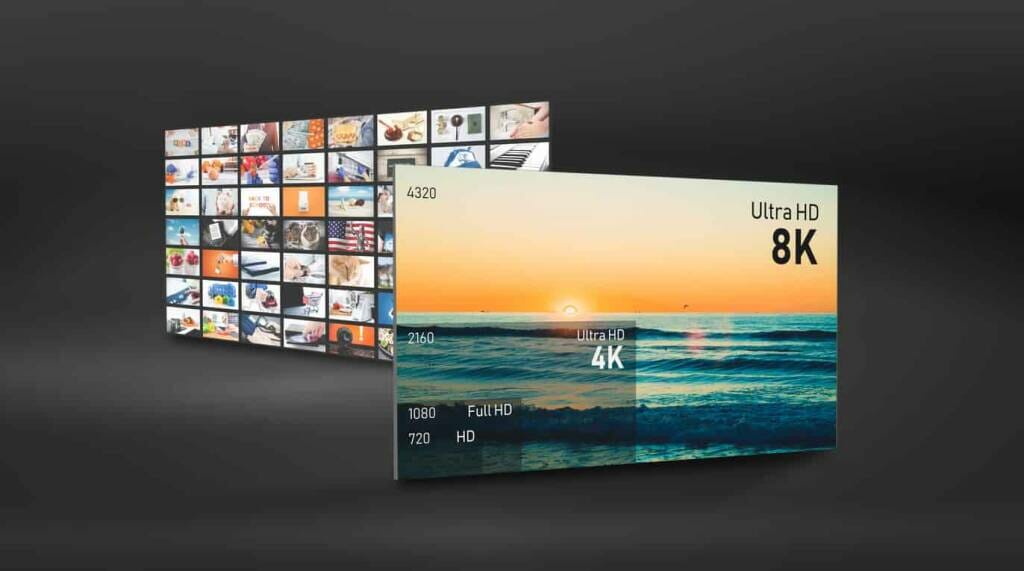
While SD vs HD quality is often the focus for most broadcasters, it’s important to note that 4K streaming offers even higher resolution than HD, delivering four times the pixels of 1080p HD. 4K streaming has become the gold standard in terms of visual quality, with resolutions such as 3840 x 2160 pixels or 4096 x 2160. However, it requires substantial bandwidth, making it more suitable for devices that support OTT streaming (over-the-top streaming via the internet) rather than traditional satellite or cable TV.
4K is currently the highest available resolution for streaming, but its widespread adoption is still limited. Most devices, especially mobile ones, are not yet capable of fully displaying true 4K content. For now, 4K is primarily reserved for larger screens like TVs and high-end monitors.
Does SD vs. HD Matter for Streaming?


The choice between SD vs HD streaming can significantly impact the viewer experience. So, which is better for streaming: SD or HD? The answer depends on several factors, but ultimately, yes—it does matter. Both formats come with their own advantages and drawbacks, and making the right choice is crucial for providing an optimal experience.
As a broadcaster, ensuring your viewers have the best experience is paramount. Whether you’re streaming content to generate revenue or build a loyal audience, the quality of your live stream reflects on your brand. That’s why understanding the difference between SD and HD streaming is so important.
While high resolution doesn’t automatically guarantee better quality, the rise of fast, reliable internet means many viewers now have the bandwidth to support HD streaming. With the growing availability of high-speed connections, it’s worth considering HD vs SD bandwidth usage. HD streaming requires higher bandwidth because it transmits at a higher bitrate, which can put a strain on networks with limited speeds.
However, the investment in HD streaming is often worthwhile for broadcasters aiming to provide an immersive, top-notch viewing experience. HD video quality offers a sharper, more detailed image, which is ideal for content where visual clarity is key—whether it’s a live event, sports broadcast, or premium production.
On the other hand, SD streaming still has its place, especially in environments where bandwidth is limited or for content that doesn’t rely heavily on visual detail. SD streaming benefits include lower data usage, making it more accessible to users with slower internet connections or mobile data restrictions.
The bottom line is that if the majority of your audience has access to reliable internet, the decision should be clear: HD streaming is generally the better option. In the ongoing debate of streaming in HD vs SD, streaming in HD delivers superior SD vs HD quality. It offers a more engaging experience for your viewers, making it the preferred choice for most modern broadcasts.
How to Stream in HD
Streaming in HD requires more than just a good camera—it involves the right setup across multiple components, including your internet connection and streaming platform. If your system isn’t up to the task, streaming in HD may not be feasible. Fortunately, most online video players, such as Dacast, support HD streaming and higher resolutions.
One of the most crucial factors for streaming in HD vs SD is your internet speed, and it’s often more important than your viewers’ connection speeds. To ensure a smooth HD stream, your upload speed must be at least double the bandwidth usage you intend to use for the stream.
Here are some general guidelines for Internet speed and HD streaming requirements:
- 25 Mbps: sufficient for streaming 1080p HD video
- 10 Mbps: sufficient for 720p video
- 5 Mbps: sufficient for 480p video
You can easily check your internet speed with tools like Google’s speed test. Just search for “internet speed test” to get a reading of your connection’s current performance.
To ensure optimal SD vs HD quality, you also need to configure your encoder correctly. This includes setting the appropriate bitrate and resolution for your stream. A properly tuned encoder helps ensure that your stream delivers the desired clarity and smoothness, particularly for higher resolutions like 1080p HD.
How are Resolution and Bitrate Related?


In HD vs SD streaming, bitrate and resolution go hand in hand. While resolution determines the clarity of your video, bitrate controls how much data is transmitted per second, directly impacting both video quality and the smoothness of your stream. Together, they play a crucial role in the overall quality of the stream and the experience for your viewers.
Bitrate and Resolution Settings for Streaming in Different Definitions
Video bitrate is the amount of data used to encode a video, typically measured in kilobits per second (kbps). A higher bitrate means more data is being transferred, allowing for higher-quality visuals, but it also requires more bandwidth to maintain smooth playback. Similarly, the resolution determines the sharpness of your video. Higher resolution equals more pixels, which creates a crisper, clearer image. However, increasing the resolution often requires a higher bitrate to maintain quality without buffering.
To put this into perspective, here’s a breakdown of recommended bitrate and resolution settings for different streaming definitions on platforms like Dacast:
| ULD | LD | SD | HD | FHD | |
| Name | Ultra-Low Definition | Low Definition | Standard Definition | High Definition | Full High Definition |
| Video Bitrate (kbps) | 350 | 350 – 800 | 800 – 1200 | 1200 – 1900 | 1900 – 4500 |
| Resolution Width (px) | 426 | 640 | 854 | 1280 | 1920 |
| Resolution Height (px) | 240 | 360 | 480 | 720 | 1080 |
| H.264 Profile | Main | Main | High | High | High |
As you can see, higher resolutions, such as HD streaming, require higher bitrates to maintain quality. For example, streaming in HD typically requires a bitrate between 1200 and 1900 kbps, whereas SD streaming can operate with a much lower bitrate, ranging from 800 to 1200 kbps.
For additional recommended and required encoder settings, please check out our dedicated post on encoder configurations.
Multi-Bitrate Streaming

One of the most powerful tools for making HD streaming accessible to more viewers is multi-bitrate streaming. With this technique, broadcasters create multiple versions (or “renditions”) of a video at different bitrates. They are created through a process called “transcoding,” allowing viewers with varying internet speeds to access the optimal version for their connection.
This is where adaptive bitrate players come in. With an adaptive bitrate video player, the video automatically adjusts to the viewer’s internet speed, providing the best possible quality without any buffering or interruptions. This is particularly useful in the debate of SD vs HD streaming, as it ensures a seamless experience for all viewers, regardless of their connection quality.
Multi-bitrate streaming with an adaptive video player takes this to the next level. With an adaptive HTML5 video player, viewers are automatically served the optimal rendition for their internet speed. This enhances the user experience because the viewers can access the best video quality possible without making any manual indications.
Detailed Technical Specifications
To get a better understanding of the pros and cons of HD and SD streaming, let’s discuss some of the detailed technical specifications.
Color Depth and Sampling
When comparing SD vs HD quality, one of the most noticeable differences lies in the color depth and chroma subsampling. These two factors significantly impact how colors are represented and how the image appears to viewers.
- Color Depth refers to the number of bits used to represent the color of a single pixel. SD content typically uses 8-bit color depth, which offers 256 shades of red, green, and blue (RGB). This is adequate for basic viewing but can sometimes result in visible banding, especially in scenes with subtle color transitions.
- HD streaming (and above) often uses 10-bit or even 12-bit color depth, providing a much wider range of colors—over 1 billion possible colors. This enhanced depth results in smoother gradients, more vibrant colors, and more accurate skin tones, making HD streaming more visually immersive.
- Chroma Subsampling is another aspect of color representation. Most SD content uses 4:2:0 chroma subsampling, which reduces the amount of color information to save bandwidth. While sufficient for lower resolution, this can cause color bleeding and reduced detail in HD content.
HD video typically uses 4:2:2 or 4:4:4 subsampling, preserving more color data and improving the overall image clarity and sharpness. 4:4:4 is especially preferred for professional broadcasting, as it retains the most detailed color information.
Frame Rates
The frame rate, or the number of frames displayed per second (fps), plays a crucial role in how motion is portrayed in video. SD vs HD resolution comparison typically shows the following differences in frame rates:
- SD streaming: Standard frame rates for SD broadcasts are 25 fps (PAL) or 30 fps (NTSC). These rates are typically sufficient for traditional television broadcasts or content that doesn’t involve fast-moving scenes.
- HD streaming: HD content generally supports 30 fps, 60 fps, and even 120 fps for smoother motion in fast-paced scenarios like sports or action scenes. A higher frame rate in HD streaming ensures more fluid and lifelike motion portrayal, making it essential for content that requires high precision in movement, such as gaming, sports events, or concerts.
Higher frame rates are particularly important for maintaining a seamless viewing experience in HD streaming, as they reduce motion blur and improve visual clarity. For broadcasters, especially in live streaming, using higher frame rates ensures that the stream captures every detail in real time, which is critical for audience engagement.
Now, it’s time to check out some bandwidth and compression considerations. This will help you get a clearer picture of the required compression techniques and ABR.
Advanced Compression Techniques
One of the primary challenges in streaming in HD vs SD is managing the increased bandwidth demand. HD streaming requires more data transfer, which can strain both the broadcaster’s network and the viewer’s connection.
Modern compression techniques have significantly improved the efficiency of video streaming:
- H.265 (HEVC): This codec is highly efficient, offering approximately 50% better compression than H.264 (the older standard), allowing broadcasters to stream high-quality HD content with less bandwidth. This is especially crucial for HD vs SD bandwidth usage comparisons, as H.265 reduces the load on both the broadcaster’s upload and the viewer’s download speeds without compromising image quality.
- AV1: A newer video codec designed for even greater efficiency than H.265, AV1 offers superior compression and better quality at lower bitrates. It is especially effective for 4K streaming, offering 20-30% better compression than HEVC. However, the widespread adoption of AV1 is still in progress as support for AV1 increases across devices.
Adaptive Bitrate Streaming (ABR)
To address the challenge of fluctuating network conditions, Adaptive Bitrate Streaming (ABR) is a key strategy in modern streaming technologies. ABR dynamically adjusts the video quality based on the viewer’s internet speed.
For instance, viewers with strong internet connections may receive HD streaming, while those with slower connections will automatically be switched to a lower resolution, like SD streaming, to avoid buffering.
ABR works by encoding multiple versions of the video at different bitrates, allowing the adaptive player to deliver the best possible experience. The player evaluates the viewer’s bandwidth in real time and chooses the optimal bitrate, switching seamlessly between quality levels as the connection changes.
Infrastructure and Equipment Requirements
Broadcasters can create a reliable setup for delivering high-definition content with minimal interruptions. This can easily be done by understanding the HD streaming requirements for both hardware and network infrastructure.
Hardware Specifications for HD Streaming
To deliver high-quality streaming in HD, broadcasters need to ensure their equipment is capable of handling higher resolution and bitrate demands. Here are some essential upgrades:
- Cameras: For professional-quality HD streaming, broadcasters need 1080p or 4K cameras. These cameras should support high frame rates for smooth motion (e.g., 60fps) and ensure clear image capture, especially for fast-moving content like sports.
- Encoders: An encoder converts the raw video feed into a digital stream suitable for transmission. For HD streaming, broadcasters will need encoders capable of handling higher bitrates (1.5-4.5 Mbps for HD), with support for modern codecs like H.265 or AV1.
- Storage Solutions: High-definition video requires more storage space. For efficient broadcasting, it’s essential to have high-capacity, fast storage systems that can handle large video files, both for live streaming and for archiving footage.
Network Infrastructure
A robust network is the backbone of any successful HD broadcast. Broadcasters need to ensure their network infrastructure is up to the task:
- Upload Speeds: For HD streaming, the upload speed of the broadcaster’s network must be sufficient to handle the bitrate of the stream. For example, to stream 1080p HD, you should have at least a 10-15 Mbps upload speed to accommodate the data load.
- Latency Considerations: Low latency is crucial for live events, ensuring that viewers receive real-time content. For broadcasters, this means investing in high-performance network solutions that minimize lag.
- Redundancy Planning: To avoid disruptions, broadcasters should have a redundant network setup, including backup internet connections and multiple encoders. This ensures continuous streaming even if one link fails, preventing potential downtime.
AI Innovations in HD and SD Streaming
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is playing an increasingly vital role in the evolution of both HD and SD streaming, driving improvements in video quality, compression efficiency, and user experience. One of the key areas where AI is transforming streaming is in AI-powered video compression. Traditional codecs like H.265 (HEVC) and AV1 are already improving compression efficiency for HD content, but AI-driven advancements are taking these technologies to the next level.
AI-enhanced perceptual video coding (PVC) is a perfect example of this. PVC analyzes human visual perception to discard data that the human eye cannot detect, saving bandwidth without compromising the visual quality of the stream. Furthermore, AI-based real-time bitrate optimization is revolutionizing how streaming platforms balance video quality and bandwidth usage. By dynamically adjusting compression during playback, AI ensures that the stream remains high-quality while adapting to changing network conditions, thus enhancing the overall viewing experience.
Upscaling from SD to HD
AI is also making waves in AI-powered upscaling from SD to HD. Tools like Topaz Video Enhance AI, NVIDIA’s DLSS, and Google’s AI-based Super-Resolution use machine learning algorithms. With their help, they intelligently upscale lower-resolution content to HD or even 4K, improving sharpness and reducing visual artifacts.
This innovation is particularly useful for broadcasters and over-the-top (OTT) platforms that work with legacy SD content or archival footage. AI-driven upscaling ensures that older content can be viewed in higher resolutions. This way, there is no need for a complete remaster, offering broadcasters the chance to maximize the value of their existing media libraries.
ABR and Streaming Optimization
The impact of AI also extends to adaptive bitrate streaming (ABR) and streaming optimization. AI-driven ABR technologies enable a seamless transition between SD and HD resolutions, adjusting the quality based on real-time network conditions and device capabilities.
AI can proactively adjust the video quality before buffering occurs by predicting potential network congestion, ensuring smooth playback. This predictive capability is enhanced by AI-powered Content Delivery Networks (CDNs), which optimize the delivery of streams, reducing video latency and improving load times.
Predictive Analytics for Streaming Quality
In addition, AI-based predictive analytics is improving streaming quality by predicting bandwidth fluctuations and advising whether to stream in SD or HD based on real-time data. This allows broadcasters to avoid streaming hiccups by optimizing the resolution depending on network stability and viewer engagement.
AI can also analyze how viewers engage with different video resolutions. This helps broadcasters determine when and where it makes sense to prioritize HD streaming over SD, based on demand and available bandwidth.
Real-Time Video Enhancement
AI-powered real-time video enhancement technologies are also pushing the boundaries of HD and SD streaming. AI tools for denoising, sharpening, and HDR conversion improve the quality of live streams by enhancing image clarity, reducing noise, and providing more vivid colors.
AI can even dynamically adjust key features, such as faces or objects in a broadcast, improving focus during live interviews or sports events. This real-time enhancement ensures that both HD and SD streams appear at their best, even under challenging conditions.
Cloud-Based Video Encoding
The advent of AI and cloud-based video encoding has significantly streamlined the encoding process for broadcasters. Platforms like AWS Elemental and Google Video AI use AI to optimize encoding decisions based on the content type and the target audience. By automating transcoding decisions, AI eliminates the need for manual configuration of bitrate, resolution, and encoding settings, saving time and resources for content creators.
Real-Time Content Moderation and Compliance
AI is also revolutionizing content moderation and compliance with the rise of AI-powered real-time content moderation. With real-time detection of sensitive content, AI ensures that broadcasters comply with regulations by automatically blurring or censoring inappropriate material. Furthermore, AI-powered auto-captioning and language translation provide real-time, high-quality subtitles, significantly improving accessibility for global audiences and those with hearing impairments.
Video Security and Anti-Piracy in HD Streams
On the matters of security, AI for video security and anti-piracy is protecting high-definition streams from unauthorized distribution. AI-powered watermarking and content recognition technologies can track HD content in real time, preventing piracy by flagging or even adjusting quality for unauthorized viewers. AI can lower the quality for those attempting to access pirated streams, maintain HD quality for legitimate users, and safeguard intellectual property.
4K/8K Future Streaming
Lastly, AI is laying the groundwork for the future of 4K and 8K streaming. As demand for ultra-high-definition content increases, AI technologies are making 4K and 8K streaming more viable by enhancing compression, reducing buffering, and optimizing content delivery networks.
One remarkable AI-driven innovation is real-time frame interpolation, which adds extra frames to video playback, making high-resolution streams smoother and more efficient. This technology reduces the strain on bandwidth and ensures that even 4K and 8K streams can be delivered with minimal buffering, setting the stage for the next generation of streaming content.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between HD and SD streaming is straightforward. Essentially, HD streaming offers significantly higher resolution than SD, resulting in a clearer, more detailed video and a superior viewing experience. It is ideal for content where quality matters, such as live events, movies, and sports, whereas SD may still be a good option for content where visual clarity isn’t as critical or when bandwidth limitations are a concern.
With Dacast, you have the flexibility to stream in resolutions ranging from ultra-low definition to full high definition. The quality of your stream primarily depends on your encoder settings, which allow you to tailor the streaming experience to your needs.
If you’re looking for a reliable live-streaming platform that offers this level of flexibility and more, we invite you to try Dacast. With our 14-day free trial, you can explore all the professional features we offer and see how our online video platform can enhance your streaming.
You can try Dacast and all its features by signing up for our 14-day free trial today.
For more tips and updates on live streaming, we invite you to join our LinkedIn group.

 Connect
Connect
 Events
Events Business
Business Organizations
Organizations Entertainment and Media
Entertainment and Media API
API Tools
Tools Learning Center
Learning Center Support
Support Support Articles
Support Articles