OTT Deployment in the Cloud – What Broadcasters Need to Know in 2025
Broadcasters face significant challenges in the current digital industry in building scalable video streaming infrastructure. The surge in online viewership in the past year has put immense pressure on traditional streaming workflows. These often struggle to handle sudden spikes in viewers. Buffering, dropped connections, and a frustrating user experience are the results of these issues.
OTT cloud solutions offer broadcasters the possibility to ensure service continuity, enhance Quality of Experience, and meet the demands of growing audiences efficiently and at a more affordable price. Many brands are adopting OTT cloud platforms for their scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Private cloud video delivery also plays a key role in creating a more secure and adaptable infrastructure.
Join us as we explore how cloud video streaming works, the basics of OTT broadcasting, and how OTT media delivery can support both Video on Demand (VOD) and live events. We’ll also discuss how these technologies can come together to create a more modern and reliable streaming infrastructure.
Table of Contents
- How Cloud Streaming Works
- What is OTT (Over-The-Top)?
- How Does OTT Streaming Work?
- The Difference Between OTT Providers And Platforms
- Comparison of Cloud vs. On-Premise OTT Infrastructure
- OTT for VOD vs. Live Streaming
- Cloud-Based OTT Streaming
- OTT Cloud Industry Trends
- Guide to Choosing the Right OTT Cloud Provider
- Future of OTT Cloud and Cloud-Native OTT
- FAQs
- Conclusion
How Cloud Streaming Works
Cloud video allows brands to deliver video content using a network of servers dedicated to cloud hosting. Unlike traditional streaming infrastructure, which requires heavy upfront investment and ongoing maintenance, cloud streaming leverages the scalability and flexibility of cloud computing.
A major benefit of private cloud video delivery is the ability to host video content closer to viewers by distributing infrastructure across the globe. This will reduce the latency and improve the overall streaming experience by using the web to directly deliver content to viewers, bypassing traditional cable and satellite providers. It’s a method that transforms how we consume media and enables faster access and better scalability.
As the audience of a brand grows, live-streaming servers can quickly scale to handle the demand. This ensures that the viewers receive content with minimal buffering or interruptions. Over-the-top video cloud solutions eliminate most of these drawbacks by leveraging on-demand cloud computing resources.
Most streaming platforms are capable of ingesting a variety of video files and transcoding them in the cloud. These files get rendered into formats more suitable for transfer to end-users and are hosted on cloud servers, so they’re ready for delivery.
With cloud streaming, brands can eliminate the need for on-premise infrastructure and make OTT broadcasting more straightforward. Transcoding and other tasks are resource-intensive, so the ability to quickly scale across more cloud servers makes cloud streaming an efficient method for meeting demand as a brand’s audience grows.
What is OTT (Over-The-Top)?

OTT (over-the-top) streaming is a way of delivering media content directly to viewers via the public Internet, bypassing traditional cable, broadcasts, and satellite services. This approach allows viewers to access content whenever and wherever they choose without being tied to specific broadcasting schedules.
OTT streaming offers more control over content delivery, as broadcasters no longer need to rely on proprietary hardware or network gatekeepers. Instead, they can deliver video directly to devices such as laptops, smartphones, tablets, and Smart TVs via internet connections.
For consumers, OTT streaming offers an alternative to traditional cable or satellite subscriptions, often at a lower price point. They can enjoy video-on-demand (VOD) content and have the flexibility to watch their favorite shows or events on their preferred devices. This shift in viewing habits is driving the rapid growth of OTT streaming.
How Does OTT Streaming Work?
OTT is a technology-agnostic approach to content delivery that reduces costs and expands viewership using OTT technology-compatible devices, including laptops, smartphones, tablets, Smart TVs, and more.
More specifically, OTT streaming requires encoding or transcoding video files into formats suitable for delivery. It relies on cloud-based video streaming platforms or live streaming services to function. These platforms handle the heavy lifting of encoding or transcoding video files into formats suitable for delivery over the Internet.
HLS and MPEG-DASH are streaming protocols that efficiently transfer video files over a standard Internet connection. This includes breaking down large video files into chunks, so video players can progressively download these files during playback.
Advanced OTT also often includes adaptive bitrate (ABR) streaming, the way broadcasters further optimize video playback by offering streaming to multiple platforms at varying bitrates or qualities. An adaptive video player can automatically adjust the stream quality up or down in real time based on network conditions to eliminate buffering or other interruptions.
The Difference Between OTT Providers And Platforms
OTT providers, such as Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Hulu, and Disney+, are the content services consumers interact with as viewers. These companies curate their own libraries, blending original productions like Netflix’s Stranger Things or Hulu’s The Handmaid’s Tale with licensed content from other studios and distributors. Their role extends beyond simply streaming content—they build robust brand identities and provide unique viewer experiences, often tailored with features like AI-driven recommendation systems or exclusive viewing options like watch parties.
However, these OTT providers don’t operate in isolation—they rely on OTT platforms to power their content delivery. OTT platforms serve as the backbone of these streaming services, enabling the technical processes required to distribute content seamlessly over the internet. For instance, they manage the ingestion of raw video files, encoding and transcoding them into formats suitable for distribution to a wide range of devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and smart TVs.
Examples of OTT Platforms
OTT platforms provide the infrastructure and tools needed for organizations to launch their own branded streaming services. Some well-known examples include:
- Dacast: A comprehensive video hosting and live streaming platform offering features like adaptive bitrate streaming, monetization tools, and built-in analytics.
- Brightcove: Known for its robust video cloud solution, Brightcove offers a suite of tools for video hosting, OTT app development, and audience engagement.
- Vimeo OTT: A platform tailored for creators looking to monetize their content through subscriptions, rentals, or purchases.
- Kaltura: A flexible OTT platform designed for educational institutions, media companies, and enterprises, with customizable tools for video-on-demand (VOD) and live streaming.
- Wowza: Offers end-to-end streaming solutions for live and on-demand video, with a focus on scalability and low latency.
Why OTT Platforms Matter for Businesses
Unlike OTT providers, which are primarily consumer-facing, OTT platforms empower brands, businesses, and organizations to build custom streaming services tailored to their audience’s needs. For example:
- A fitness brand might use an OTT platform to create an on-demand library of workout videos accessible via subscription.
- Churches can use OTT platforms to stream live worship services and maintain archives for later viewing.
- A film studio could monetize its indie movie library through a branded, linear OTT channel.
OTT platforms offer scalability, flexibility, and control, enabling broadcasters to manage their content, delivery, and audience engagement while staying independent of the limitations set by mainstream OTT providers. By providing tools for encoding, transcoding, live stream recording, adaptive playback, and advanced analytics, these platforms equip businesses with everything they need to thrive in the competitive world of streaming.
Comparison of Cloud vs. On-Premise OTT Infrastructure
There are key differences between OTT cloud services and traditional on-premise OTT solutions, which broadcasters should consider. To help visualize them, we have prepared a comparison table that highlights the superiority of OTT cloud solutions based on various features.
| Feature | OTT Cloud Services | On-Premise OTT Solutions |
| Scalability | Easy to scale with demand | Limited by physical hardware investment |
| Upfront Costs | Lower, subscription-based | High, requires significant hardware |
| Flexibility | Highly adaptable, easy to add new features | Rigid, requires hardware upgrades for new features |
| Maintenance | Handled by service providers | Requires internal teams to manage and maintain |
| Time to Deploy | Faster, due to lack of hardware requirements | Slower, due to physical infrastructure setup |
| Content | Integrated with cloud services | May require separate systems |
OTT For VOD vs. Live Streaming
Hearing OTT is often an immediate association of on-demand content providers like Amazon and Netflix, but OTT solution providers can also be used for live events. Most OTT platforms are meant to be comprehensive video streaming solutions, so they often include features for both VOD and live streaming out of the box.
VOD Streaming
VOD streaming gives viewers full control over the video content they watch, and many brands offer a content overview for their audience to browse, download, and watch. Many VOD platforms also offer TV or DVR-like features such as fast-forwarding, rewinding, and closed captions to improve the viewing experience.
The VOD libraries often include shows, movies, webinars, or other pre-recorded content. It’s particularly popular for entertainment, education, and other types of videos that content creators want to review and edit before publishing.
An OTT platform with VOD capabilities often includes video hosting and video content management capabilities that enable brands to efficiently manage and distribute their content to generate revenue. This includes features such as library organizations and playlists.
The robust OTT software also has various monetization tools for monetizing VOD content delivery and includes the following:
There should also be a secure paywall system to accept payments and enterprise-grade security to ensure the brand’s content remains safe.
Live Streaming
Live-streaming platforms use this method to create unique, interactive experiences, which include chat and other audience interaction tools. It’s a great way to ask questions or offer feedback to the event host.
This is why live streaming is a great way for brands to build a connection with their audience and create a buzz around their content. It’s also the reason live streaming is often used for broadcasting live sports, corporate events, or virtual church services.
Live streaming is often more difficult than VOD streaming because viewers can stop watching if any issues occur. This is why broadcasters need a reliable Internet connection and an RTMP encoder that can compress and prepare RAW video files for delivery. If the connection upload speed isn’t high enough, viewers could experience quality issues.
Hosting live events may be challenging, but keep in mind that viewers are still highly sensitive to buffering and quality issues. Broadcasters need streaming infrastructure that can deliver content with very little buffering or lag time to keep viewers happy.
Along with VOD, many OTT video solutions also include live streaming capabilities. These features include automatic transcoding of live streams for delivery to a wide range of devices and real-time analytics to monitor the stream’s performance. Live stream recording allows brands to save their live events for backups or playback later on.
Cloud-Based OTT Streaming

OTT broadcasting using on-premise streaming servers comes with certain drawbacks. That’s because broadcasters must build complex streaming workflows with enough computing power to successfully deliver a video to their end-users without interruptions. Many brands are turning to OTT cloud services because scaling this on-premise infrastructure is challenging. A private cloud video delivery system provides flexibility and scalability, making it a popular choice over traditional methods.
What Is OTT Cloud?
The OTT cloud platform combines streamlined video delivery over the Internet with the scalability and flexibility of cloud technologies. For example, an online video platform (OVP) can use content delivery networks (CDNs) to reduce the load on streaming servers and provide content to end-users more efficiently. These CDNs act as traffic distributors, ensuring viewers receive livestream videos from the closest server, reducing strain on the main streaming servers and speeding up delivery.
By leveraging live streaming CDNs, an OTT cloud solution can reduce the distance live streams must travel to reach viewers by using edge servers throughout the world. This can assist broadcasters in achieving low-latency streaming and considerably improving the quality of experience for their viewers. These OTT cloud TV workflows can also provide significantly improved service continuity. That’s because cloud streaming technology is easier to replicate for redundancy and availability than on-premise video infrastructure.
What Is Cloud Native OTT?
While cloud video platforms offer improved scalability and resiliency, some platforms take it a step further with cloud-native OTT. Cloud-native software is deployed in a container environment, where the application’s individual functions are split into separate microservices.
These cloud-native applications use containerized microservices to automatically scale the application’s individual components to avoid bottlenecks. This is achieved through orchestration platforms. This means that an OTT infrastructure can optimize its resources for uploading, transcoding, or streaming tasks as necessary. This architecture is also elastic, meaning that provisioned computing resources will closely match current demand, which can lead to considerable cost savings for many enterprises.
Benefits of OTT Cloud Services
An OTT cloud TV offer several advantages over traditional on-premise setups. These advantages make cloud-based OTT platforms a game-changer for brands seeking efficient and scalable solutions for content delivery. Some of the key benefits include:
- Scalability: OTT cloud services offer the ability to scale seamlessly as demand grows. Contrary to this, traditional on-premise systems require significant upfront investments in hardware, which limits scalability. Whether you’re delivering content to a few thousand viewers or millions, the cloud can accommodate fluctuations without the need for additional hardware.
- Lower Upfront Costs: OTT cloud solutions reduce the need for costly hardware installations, allowing brands to minimize initial investments. Instead, businesses can opt for a subscription-based model, paying for what they use and reducing capital expenditure (CAPEX).
- Flexibility: Cloud-based platforms offer a high level of flexibility, allowing businesses to adapt quickly to changing market demands and changing viewer habits. You can easily add new features or services without the constraints of physical infrastructure.
- Reduced Maintenance: With cloud OTT solutions, the burden of server management and maintenance is shifted to the cloud service provider. This frees up internal resources and allows businesses to focus on delivering high-quality content.
Key Features to Look for in OTT Cloud Services
When evaluating OTT cloud services, certain features are essential to ensure the best performance and user experience. Each of these features plays a vital role in ensuring the success of your OTT environment and includes:
- CDN Support: A Content Delivery Network (CDN) integration that ensures fast and reliable content delivery worldwide.
- Adaptive Bitrate Streaming: It adjusts video streaming quality based on the viewer’s internet connection, ensuring smooth playback.
- Security: Protect your content and user data by using encryption, secure APIs, and user authentication.
- Reliability: The OTT cloud platform should offer strong uptime guarantees, strong backup systems to minimize downtime, and proven reliability in high-traffic situations.
Comparison of Major OTT Cloud Providers
We have prepared a brief comparison of some major OTT cloud providers, highlighting how different providers stack up in terms of pricing, scalability, and support, helping you make a more informed decision.
| Provider | Pricing | Scalability | Customer Support |
| Dacast | Flexible Plans (monthly or pay-as-you-go) | Seamless scalable with global CDN integration | 24/7 dedicated support and live chat at all plan levels |
| Google Cloud | Flexible pricing plans | Easily scalable | Multi-tiered support |
| AWS | Pay-as-you-go | Highly scalable | 24/7 global support |
| IBM Cloud | Subscription-based | Scalable | Comprehensive support |
Challenges with On-Premise OTT Solutions and How OTT Cloud Addresses Them
Traditional on-premise OTT solutions come with several challenges, and OTT cloud services resolve these issues by offering flexible, cost-efficient, and easily scalable solutions. Because the need for physical hardware is eliminated, businesses can scale on demand without the heavy burden.
- Hardware Maintenance: On-premise infrastructure requires continuous hardware maintenance, which can be costly and resource-intensive. OTT cloud services eliminate the need for physical servers.
- High Capital Expenditure (CAPEX): Setting up and maintaining an on-premise OTT app requires significant upfront investment in hardware and infrastructure. Cloud services minimize CAPEX by operating on a subscription or pay-as-you-go basis.
- Difficulty Scaling: Scaling on-premise infrastructure can be costly and slow as the audience grows because it involves purchasing additional hardware. This can delay growth and increase costs, which is why cloud services offer near-instant scalability.
Who Should Use Cloud OTT Platforms?
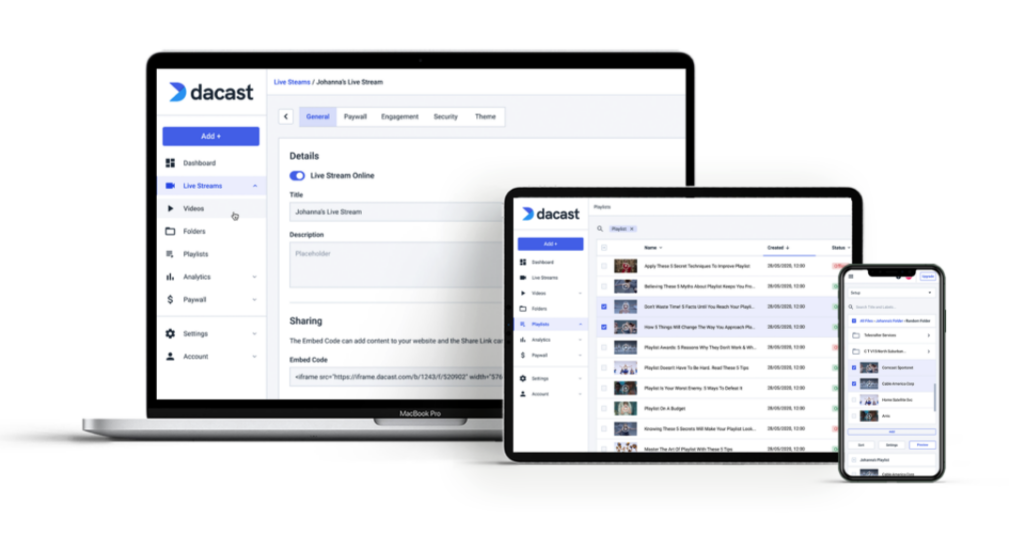
Online OTT cloud platforms are great for brands that want to launch and scale video streaming efforts quickly. Investing in OTT platforms with end-to-end video streaming allows businesses to refocus their efforts on core business objectives. This way, they can concentrate on producing high-quality content for their audience without worrying about hardware, technical challenges, and infrastructure scaling. Brands can simply upload videos to their OVP platform and, with a few configurations, deliver VOD or live-streaming content directly to their audience at an affordable price.
Many OTT platforms also give brands complete control over distribution. For example, broadcasters can use a white-label video player to customize the viewing experience to ensure it’s on-brand. Comprehensive video APIs also allow enterprises to integrate video content and cloud streaming functionality into their own mobile apps, websites, and more.
It’s no wonder, then, why OTT video streaming platforms are ideal for brands that want to build professional broadcasting workflows for VOD and live broadcasting without worrying about on-premise infrastructure or other technical requirements.
Use-Case Examples of Successful Use of OTT Cloud Services
Several companies have successfully transitioned to OTT cloud platforms, reaping significant benefits in performance, scalability, and audience reach. These examples highlight how OTT cloud solutions can improve performance and expand audience reach, setting brands up for success.
- Netflix: One of the pioneers in adopting OTT cloud streaming technology, Netflix transitioned to a cloud-based OTT solution to handle its massive global audience. The shift to the cloud allowed Netflix to scale quickly and effortlessly, handle peak traffic, deliver content across multiple regions without interruptions, and offer personalized content recommendations using AI.
- Disney+: Using an OTT cloud platform, Disney+ managed to handle a massive influx of subscribers upon its launch and ensures a seamless viewing experience across millions of users worldwide. By using a cloud OTT platform, Disney+. The cloud infrastructure enabled the platform to expand rapidly while maintaining high performance.
- Hulu: Hulu migrated to a cloud environment to enhance its content delivery network (CDN) performance and ensure better scalability. The result? Hulu can now deliver both live TV and on-demand content with fewer interruptions and faster response times.
OTT Cloud Industry Trends
New technological advancements and market demands drive a rapid evolution of over-the-top cloud services. Staying ahead of the latest OTT trends will allow brands to maximize the potential of their OTT cloud platforms and deliver superior streaming experiences.
- Many businesses are adopting multi-cloud environments to improve redundancy, flexibility, and better performance. This allows them to distribute content more efficiently.
- To curate content for individual users, OTT platforms use artificial intelligence to deliver personalized content recommendations based on viewer habits, enhancing user experience and engagement.
- Greater emphasis is put on security by using stronger DRM solutions and secure payment options to protect content and user data.
- Subscription fatigue encourages the development of new and innovative monetization models. As alternatives, the providers are increasingly leaning towards advertising monetization and pay-per-view.
- To maximize their success, content creators are using content fragmenting to target their niche audience. The idea behind this is to carefully select content and set it up strategically for delivery.
- Offering users to experience content in a new and immersive way is done through the integration of augmented and virtual reality into OTT platforms.
- The 5G networks had a great impact on OTT cloud streaming technology. It is set to become faster, allowing for higher-quality streams and improved user experience.
Guide to Choosing the Right OTT Cloud Provider
One might think that selecting the best OTT cloud provider is an easy task, but think again. With so many vendors out there, any tool looks just right. When choosing the right OTT Cloud provider for you, you should consider your needs and these key requirements:
- Scalability: Whether you need a cloud TV OTT platform or an on-premise OTT solution, ensure the platform can grow with your audience without performance degradation. Fulfilling your changing demands every step of the way is a key feature every cloud provider should offer. This, in turn, means you pay for what you need as opposed to inflexible cloud solutions at a higher cost.
- Security and Compliance: With data loss, leakage, and privacy, security is a concern for many. Look for providers offering strong encryption, DRM (Digital Rights Management), and compliance with industry standards. They should also offer security audits and testing to help you track user activity through logs, as well as IAM (Identity and access management) for multi-factor authentication, firewalls, role-based access, and more.
- Content Management: Always go for providers that have intuitive content management features. This will allow seamless uploading, organizing, and updating of content.
- Cost and Pricing Model: Pricing models differ between cloud providers, ranging from monthly plans to annual payments and even free options. To save money, consider choosing the right pricing model for you. To avoid paying extra, look over the data-transfer costs to find the one that matches your budget and needs. And finally, look for hidden costs like maintenance fees.
- Customer Support: Look for 24/7 customer support to avoid being stuck if you run into a problem. They come in the form of email, phone, online chat, FAQ section, user guides, etc. Check the reviews to see what others have to say, and choose the one with great customer service.
Future of OTT Cloud and Cloud-Native OTT
Looking ahead, the future of OTT cloud solutions is bright, with emerging technologies such as containerization and microservices transforming how businesses deliver content. They are improving the scalability and resilience of OTT cloud TV platforms.
As cloud streaming software continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative and efficient ways to manage and scale OTT infrastructure. It will become even more flexible, allowing businesses to deploy faster, manage complex workflows, and better serve their audiences.
An OTT cloud platform provides brands with a scalable, flexible, and cost-efficient solution for delivering content. With the industry moving toward cloud-native solutions and technologies like AI and 5G, adopting a cloud-based OTT infrastructure is a forward-looking move that will position businesses for long-term success.
FAQs
1. What does OTT mean?
OTT stands for over-the-top, and in the context of video, it means delivering video content over the internet, bypassing traditional distribution methods like cable, satellite, or broadcast TV. You can access video content directly through the internet, typically via a live streaming service.
2. How do you implement an OTT video?
Launching an OTT video requires choosing a cloud OTT platform that suits your needs. Upload your video content to the platform and configure it for streaming. This may involve encoding the videos into various formats to ensure compatibility with different devices and internet speeds. Finally, you’ll need to integrate the OTT platform with your website or app, allowing users to access the content seamlessly.
3. Which OTT platform is best for live streaming?
The best video streaming platform depends on your specific needs and budget. There are several over-the-top video cloud solutions well-suited for streaming high-quality video content. Some popular options include Dacast, Vimeo OTT, Wowza, IBM Cloud Video, and others. Each of these OTT platforms offers various tools and features tailored to video streaming needs, such as content delivery networks, on-demand video streaming, transcoding services, and scalable infrastructure.
4. Can you stream directly to the cloud?
Yes, you can stream directly to the cloud using OTT cloud-based video streaming platforms like Dacast so that you do not have to use your own storage. These platforms have tools for encoding and transmitting live video feeds to cloud servers, where they can be processed, stored, and distributed to viewers in real time.
5. Is Netflix an OTT platform?
Yes, Netflix is one of the most prominent examples of an over-the-top video streaming platform. It delivers a vast library of movies and TV shows directly to subscribers over the internet. In addition to Netflix, there are many other popular OTT platforms like Hulu, Disney+, and HBO Max.
6. Is Dacast an OTT platform solution?
Yes, Dacast is an OTT (Over-The-Top) platform solution. It provides businesses and content creators with tools to host, manage, and stream video content directly to their audience over the internet. Dacast supports live streaming, video on demand (VOD), and offers features such as monetization, analytics, and white-label services. The platform is designed for a wide range of industries, including education, entertainment, and corporate communications. It allows users to deliver content without relying on traditional broadcast methods.
Conclusion
OTT streaming has become extremely important for most brands since modern consumers want complete control over their content. OTT cloud platforms make it easier for broadcasters to get started and scale up their IT infrastructure as their audiences grow.
Dacast is an OTT cloud video platform that’s ideal for streaming video across the internet. That’s why the platform was nominated best platform for small/medium businesses (SMBs) in the 2019 Streaming Media Readers’ Choice Awards.
Are you interested in delivering video to nearly any device or audience? Try our 14-day FREE trial to see if Dacast fits your needs.
Any questions, comments, or ideas about over-the-top streaming? We love to hear from our readers, so post your thoughts in the comment section below. We will get back to you. Also, for exclusive offers and regular live streaming tips, you can join our LinkedIn group.
Thanks for reading, and as always, best of luck with your live streams!
 Stream
Stream Connect
Connect Manage
Manage Measure
Measure Events
Events Business
Business Organizations
Organizations Entertainment and Media
Entertainment and Media API
API Tools
Tools Learning Center
Learning Center Support
Support Support Articles
Support Articles