Adaptive Bitrate Streaming: What it Is and How the ABR Algorithm Works [2025 Update]
For most broadcasters, delivering a high-quality, buffer-free viewing experience is at the top of the priority list. The growth projections for the live streaming market are expected to grow exponentially, meaning broadcasters must adopt efficient streaming solutions to stay competitive. This is where adaptive bitrate streaming (ABR) comes into play.
Today’s audiences expect seamless playback, whether they’re watching on a smartphone over mobile data or on a 4K TV with a high-speed fiber connection. However, fluctuating bandwidth and network conditions and varying device capabilities make it challenging to provide a consistently high-quality stream. In fact, more than half of viewers will abandon a poor-quality stream within 90 seconds, making stream reliability a key factor in audience retention and business success.
To tackle these challenges, broadcasters rely on adaptive bitrate streaming, a technology that dynamically adjusts video quality based on real-time network conditions and device performance. By using the ABR algorithm, streaming providers can ensure optimal viewing experiences without excessive buffering or quality degradation. Whether it’s multi-bitrate live video streaming or HLS adaptive bitrate technology, implementing an effective ABR ladder is essential for delivering smooth, high-quality content across all devices.
In this article, we’ll dive into what adaptive bitrate streaming is and how it works. We’ll also look at what makes up a streaming profile and how brands can implement ABR streaming themselves.
Table of Contents
What is Adaptive Bitrate Streaming?
- How Does ABR Streaming Work?
- Adaptive High Bitrate vs. High Bitrate
- Adaptive Bitrate Streaming Algorithms
- Adaptive Bitrate Streaming Profiles
- What is the ABR Ladder?
- What is RTMP Adaptive Bitrate?
- Latest Streaming Protocols and Technologies
- How to Do Adaptive Bitrate Streaming
- The Benefits of Adaptive Playback
- Emerging ABR Solutions and Platforms
- AI-Powered Enhancements in ABR
- Future Trends and Considerations
- FAQ
- Conclusion
What is Adaptive Bitrate Streaming?
Adaptive bitrate streaming (ABR) is a crucial technology that ensures seamless playback by dynamically adjusting video quality in real time. This process allows viewers to enjoy a buffer-free experience, even when network conditions fluctuate.
To understand ABR streaming, let’s first examine the importance of bitrates in video streaming and how adaptive playback enhances the user experience.
What is a Bitrate for Streaming?
The video bitrate of a stream refers to the speed at which video data is transformed to a user’s. It is measured in megabits per second (Mbps), which differs from a video’s file size, typically measured in megabytes (MB).
In general, a higher bitrate means the video quality will be better, but if it exceeds a user’s bandwidth (also measured in Mbps), buffering can occur. Buffering happens when a video player cannot download the video file fast enough to keep the video playing at normal speed. That causes playback interruptions (e.g., the spinning loading icon).
Several factors influence a video’s bitrate and overall streaming quality:
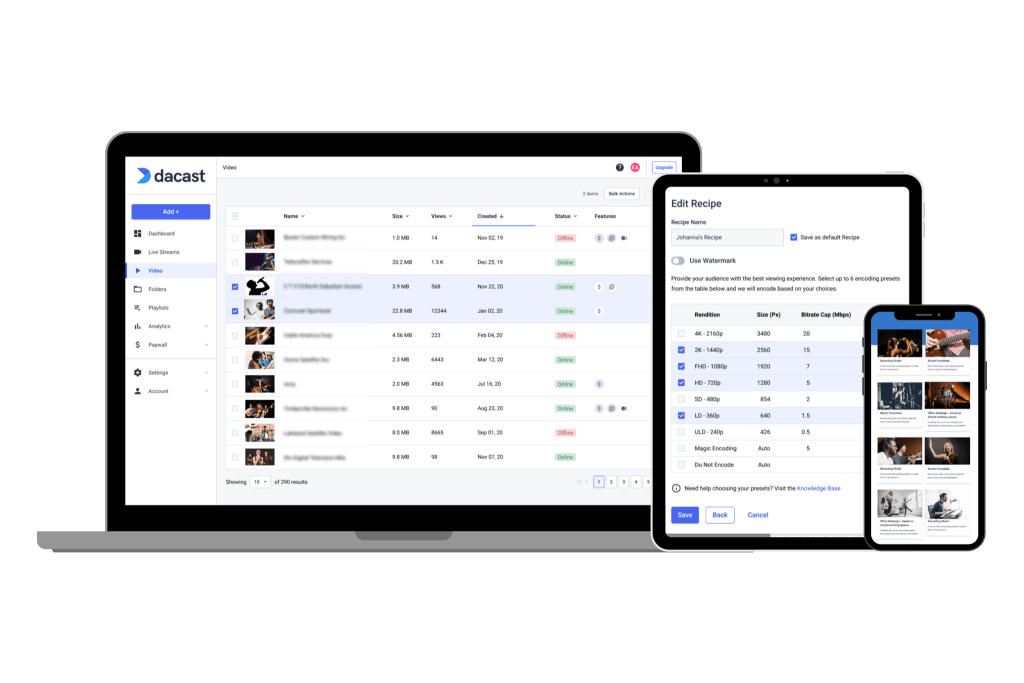
- Video resolution: The video resolution refers to the number of pixels within a frame. Higher resolutions (480p, 720p, 1080p, 4K) require more bandwidth but provide sharper images.
- Frame rate: Standard frame rates include 24 frames per second (fps) for films, but sports events or other streams require smoother playback and may use 30 to 60 fps. A higher frame rate can display motion better, but more frames also require additional data.
- Codec efficiency: A higher quality video, with a greater resolution and frame rate, generally has a higher bitrate. This is why some codecs that compress video data are more efficient than others. Newer codecs like H.264 and H.265 provide higher quality video at lower bitrates compared to older codecs.
What is Adaptive Playback?
ABR uses an intelligent algorithm to adjust video quality in real time based on network conditions and device performance. The end result is that broadcasters can offer multiple streams with different ABR bitrates to users. The video player dynamically switches between bitrate levels in response to changing network conditions, reducing buffering and maintaining playback smoothness.
In contrast, multi-bitrate streaming (MBR) offers several stream options but locks users into a selected bitrate. A sudden drop in bandwidth could lead to buffering, so MBR streaming without adaptive playback isn’t ideal for most streaming situations. Multi-bitrate streaming helps to provide viewers with a better viewing experience, but not a perfect viewing experience.
If you want to deliver high-quality streams and give viewers the best viewing experience, you will want to use ABR streaming. This is the preferred solution for modern streaming platforms.
How Does ABR Streaming Work?

Adaptive bitrate streaming ensures the best video quality an internet connection supports. By dynamically adjusting video quality based on real-time network conditions, ABR streaming enhances playback efficiency and reduces buffering.
But how exactly do broadcasters implement ABR technology? Let’s break it down into three key steps.
1. Video Preparation
Before ABR streaming can begin, video content must be prepared. This includes encoding the video at multiple bitrates to create an ABR ladder. An ABR encoder processes the video into various resolutions and bitrates, ensuring compatibility with different devices and internet speeds. Most online video platforms support ABR encoding by transcoding videos into multiple formats from a single source file.
Each encoded video file is then segmented into smaller multi-second chunks, typically ranging from 2 to 10 seconds. This segmentation is crucial for HTTP-based streaming protocols like HLS adaptive bitrate and DASH, allowing for seamless progressive downloading and playback.
2. Initial Startup
When a user starts a video, the video player first downloads a manifest file that lists the available video chunks and ABR bitrates. This manifest file is formatted as:
- M3U8 for HLS adaptive bitrate streaming
- MPD for DASH (Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP)
M3U8 files contain plain text that specifies the locations of media files, either through absolute URLs or relative paths. This manifest file contains the .m3u8 playlist for HLS and the media presentation description (MPD) for DASH, which contains the information that makes up a streaming profile.
The manifest file provides a structured overview of the available bitrate options, enabling the video player to select the best-quality stream for the user’s device and network conditions.
Because ABR streaming is HTTP-based, content can be stored and delivered efficiently via content delivery networks (CDNs). This setup significantly reduces latency, minimizes packet loss, and improves overall delivery speed.
Adaptive bitrate streaming, when paired with a global CDN network, allows broadcasters to reach viewers around the globe effectively.
3. Dynamic Playback
Once playback begins, the video player continuously assesses the user’s bandwidth and device capabilities. It requests higher or lower-quality video chunks as conditions change. Different ABR algorithms are used to determine the best bitrate selection:
- Throughput-based algorithms: Measure previous video chunk download speeds to estimate available bandwidth. However, these estimates may not always match actual encoder bitrates during live streams.
- Buffer-based algorithms: Prioritize maintaining a preloaded buffer to avoid playback interruptions. If the buffer runs low, the player lowers the bitrate to prevent stalling. The problem is knowing how far to lower the bitrate to fill the buffer without downgrading the quality too much.
- Hybrid ABR algorithms: Some advanced video players, like THEOplayer, combine throughput and buffer-based methods. They can even switch bitrates mid-download to maintain optimal playback.
Over the coming years, more advanced algorithms using machine learning may gain traction as well. AI-driven ABR algorithms will optimize bitrate selection more accurately, reducing buffering and improving video quality in real time.
Adaptive High-Bitrate vs. High Bitrate
Let’s start with answering the question “What is adaptive high bitrate?” It is a significant advancement over traditional high bitrate streaming. Unlike high bitrate streaming, which delivers video content at a constant data rate, adaptive high bitrate streaming dynamically adjusts video quality based on real-time network conditions and device capabilities. This is achieved through an adaptive bitrate streaming algorithm, which ensures smooth playback by seamlessly switching between different quality levels to match the available bandwidth.
The key advantage of adaptive high bitrate streaming is its ability to reduce buffering and enhance playback stability. An adaptive media delivery system, powered by an intelligent media player, selects the most suitable video quality from a predefined ABR ladder. This approach maintains optimal visual quality without overloading the network, unlike traditional high-bitrate streaming, which may lead to playback interruptions if the network cannot sustain the required data rate.
While high bitrate streaming offers excellent quality, high bitrate vs. adaptive high bitrate comparisons highlight that adaptive high bitrate streaming delivers superior performance by balancing quality with bandwidth efficiency. For modern video delivery, adaptive high-bitrate streaming is the preferred choice for both content providers and viewers.
Adaptive Bitrate Streaming Algorithms
Adaptive bitrate streaming algorithms are essential for delivering high-quality video content across varying network conditions. These algorithms enable ABR streaming by dynamically adjusting video resolution and bitrate in real time. A fundamental component of this system is the ABR ladder, which consists of multiple pre-encoded versions of a video at different bitrates and resolutions. This flexibility allows the algorithm to switch between these versions as needed.
Several streaming protocols use ABR encoding to provide smooth playback without buffering, even as network conditions fluctuate. These include:
- RTMP adaptive bitrate for low-latency streaming
- HLS adaptive bitrate for efficient playback across Apple devices
- DASH adaptive bitrate for adaptive streaming on various platforms
- WebRTC adaptive bitrate for real-time, low-latency streaming
The process of ABR transcoding involves creating multiple versions of a source video, each encoded at different bitrates using adaptive bitrate encoding.
An adaptive bitrate streaming player plays a central role. It continually monitors network conditions and adjusts the video stream accordingly. This intelligent approach ensures that viewers experience uninterrupted playback at the best possible quality their network can support. This enhances the overall viewer experience and satisfaction.
Adaptive Bitrate Streaming Profiles
A streaming profile defines the variations of a video that are made available for streaming. This includes different bitrates, resolutions, codecs, and formats, ensuring optimal playback across a range of devices and network conditions.
Most ABR streaming profiles follow universal ladder designs optimized for various devices and bandwidth conditions. Apple proposed a fixed bitrate encoding ladder, which Netflix later refined to maximize video quality at each level.
Another emerging strategy is context-aware encoding (CAE), which customizes the adaptive playback experience based on the user’s device type. It encodes video specifically for smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, and other devices. This way, CAE enables broadcasters to deliver higher Quality of Experience (QoE) while reducing bandwidth usage.
There is no single streaming profile that fits every broadcaster’s needs. The ideal profile depends on factors such as target audience, device compatibility, and available bandwidth. In the next section, we’ll explore best practices for selecting protocols and bitrates to optimize ABR video encoding for a seamless viewer experience.
What is the ABR Ladder?
The ABR ladder is a crucial component in ABR video streaming. It ensures a smooth and adaptable viewing experience. An ABR ladder uses multiple versions of a video, each encoded at different bitrates and resolutions through ABR video encoding. This set of varied streams allows the ABR encoder to switch easily between them based on the viewer’s network conditions and device capabilities.
In ABR encoding, video content is transcoded into several quality levels, forming the rungs of the ABR ladder. During playback, the ABR algorithm dynamically selects the most appropriate stream, providing the highest possible quality without buffering. This adaptability ensures viewers enjoy a continuous stream of high-quality viewing, even as internet connection speeds fluctuate.
What is RTMP Adaptive Bitrate?
RTMP adaptive bitrate streaming enhances the viewing experience by dynamically adjusting video quality based on real-time network conditions. RTMP (Real-Time Messaging Protocol) plays a major role in multi-bitrate live video streaming, enabling smooth video delivery with minimal buffering.
Unlike progressive video streaming, which delivers content linearly without considering network variations, RTMP adaptive bitrate streaming incorporates ABR rate control. This technique continuously monitors a viewer’s available bandwidth and device performance, allowing the streaming server to switch seamlessly between different quality levels.
The ABR rate control within RTMP adaptive bitrate streaming ensures that viewers always receive the best possible video quality available to them. With RTMP’s efficient data transport capabilities, ABR streaming becomes more reliable and resilient, continuously delivering high-quality content with reduced latency.
Latest Streaming Protocols and Technologies
Advancements in ABR streaming have introduced new protocols and technologies that enhance video delivery efficiency, reduce latency, and improve video quality. There are several key innovations shaping the future of ABR streaming.
High Efficiency Streaming Protocol (HESP)
HESP is a modern HTTP-based adaptive media delivery protocol that offers sub-second latency and ultra-fast channel switching. It is what makes it a strong competitor to Low-Latency HLS (LL-HLS) and Low-Latency DASH (LL-DASH). Unlike traditional HLS adaptive bitrate methods, HESP optimizes start-up times and reduces buffering for superior live streaming.
Enhanced RTMP (E-RTMP)
Enhanced RTMP (E-RTMP) builds upon the legacy RTMP adaptive bitrate framework by introducing support for modern video codecs like VP9, HEVC, and AV1. It also includes multitrack capabilities and improved connection resilience while maintaining backward compatibility. This ensures a more immersive multi-bitrate live video streaming experience, particularly for real-time and interactive content.
AV1 Codec Adoption
The AV1 codec has seen widespread adoption among major streaming platforms like Netflix and YouTube. This is due to its superior compression efficiency and high-quality video delivery. AV1 allows ABR video encoding to maintain excellent video quality at lower bitrates, making it an ideal choice for bandwidth-efficient ABR streaming. As a result, AV1 adoption is helping to optimize low bitrate vs high bitrate streaming performance, providing cost-effective and sustainable video delivery solutions.
How to Do Adaptive Bitrate Streaming
For broadcasters looking to implement adaptive bitrate streaming, several key decisions must be made regarding streaming protocols, bitrates, and video players. Below are the considerations for ensuring optimal ABR streaming in 2025.
Which Streaming Protocol Should I Use?
A streaming protocol dictates how audio and video are transmitted over the internet. The best video streaming protocol for your needs depends on whether you prioritize ABR or low-latency streams.
Once the dominant protocol, RTMP has now been largely deprecated for direct video delivery to end users. While RTMP was originally used to stream to Flash Player, modern browsers have universally adopted HTML5 video players instead. However, RTMP adaptive bitrate streaming is still used for transmitting video from an ABR encoder to an online video platform (OVP), making it relevant for contribution rather than playback.
Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (DASH), or MPEG-DASH, has gained significant traction due to its codec-agnostic approach, meaning it works with AV1, H.264, H.265/HEVC, and VP9. While MPEG-DASH is not natively supported by HTML5, many players integrate it via JavaScript and Media Source Extensions (MSEs) to ensure adaptive media delivery.
HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) remains the preferred protocol for HTML5 video players, particularly with HLS adaptive bitrate streaming. HLS now fully supports H.265 / HEVC and is evolving to support AV1 for superior compression and efficiency. While HLS originally used 10-second video segments, newer implementations with low-latency HLS (LL-HLS) and HESP reduce segment durations for faster adaptive playback.
What Bitrate Should I Stream At?
The best bitrates depend on your audience and the devices they use. Offering multiple bitrates ensures a seamless viewing experience across different network conditions.
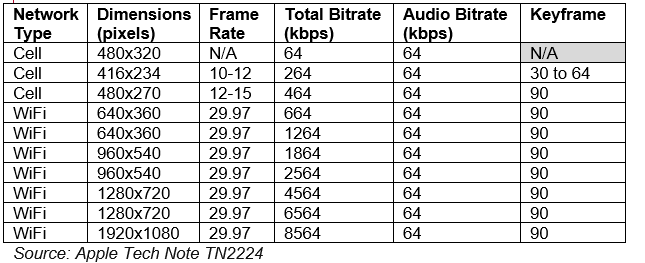
These are some commonly recommended bitrate settings:
- 360p video: 500 Kbps – 1.5 Mbps
- 480p video: 800 Kbps – 2.5 Mbps
- 720p video: 2 Mbps – 5 Mbps
- 1080p video: 4 Mbps – 8 Mbps
- 4K video (2160p): 10 Mbps – 25 Mbps (depending on codec and target devices)
At Dacast, we recommend providing a bitrate below 1000 Kbps to ensure any user can watch your videos. Additional bitrates above this will improve the viewing experience for users that have the device and bandwidth necessary. For HLS adaptive bitrate streaming, here are our suggestions when configuring the encoder.
What is Adaptive Streaming Using JavaScript?
As we mentioned earlier, the video player is essential in enabling ABR live streaming. Modern HTML5 players, such as Video.js Shaka Player, Hls.js, and other JavaScript video players, are designed to handle multi-bitrate live video streaming and adapt to changing network conditions. These players use ABR algorithms to determine the optimal video quality in real time.
Adaptive streaming with JavaScript enables dynamic video delivery by selecting:
- The best video bitrate based on network conditions
- The most suitable resolution for the user’s device
- WebRTC adaptive bitrate adjustments for real-time streaming scenarios
JavaScript-based ABR players ensure a superior viewing experience while maintaining broad device compatibility. Since they are built into modern browsers, they provide seamless adaptive playback on desktops, mobile devices, and smart TVs.
The Benefits of Adaptive Playback
The primary benefit of adaptive bitrate streaming is an enhanced Quality of Experience. Broadcasters can deliver the highest possible video quality without the risk of buffering or interruptions, even when network conditions fluctuate.
In addition to smoother playback, ABR streaming enables faster startup times. Streams typically begin with a low bitrate variant until the ABR algorithm determines the viewer’s bandwidth capacity or buffer status. This means the video starts playing immediately, reducing the risk of losing viewers due to slow load times.
Adaptive media delivery is also particularly beneficial for mobile users. In the past, limited data plans and low device processing power posed challenges for video streaming on the go. With ABR technology, mobile viewers can enjoy high-quality multi-bitrate live video streaming without excessive buffering, optimizing playback across smartphones, tablets, and other connected devices.
Another key advantage is cost efficiency. Because ABR streams use HTTP-based delivery, they are compatible with most web servers and CDNs. This eliminates the need for dedicated streaming servers and persistent connections, reducing operational costs while ensuring scalability.
Finally, a poor video experience can negatively impact brand perception, even when network issues are beyond the broadcaster’s control. That limits the opportunity for advertising and monetization down the line. That’s why ABR is crucial for today’s broadcasters. ABR streaming gives you a higher degree of control over the end-user experience.
Emerging ABR Solutions and Platforms
It’s not rare for broadcasters to use cutting-edge platforms to ensure seamless, low-latency, and high-quality video delivery. The following ABR solutions are gaining traction for their scalability, efficiency, and compatibility with modern streaming protocols.
OvenMediaEngine (OME)
OvenMediaEngine (OME) is an open-source, low-latency streaming server designed to support adaptive media delivery at scale. It offers full ABR streaming capabilities and is compatible with protocols like WebRTC adaptive bitrate, LL-HLS, and MPEG-DASH.
OME is particularly favored for its ability to handle high-definition streams efficiently. This is one of the reasons that it is a preferred choice for broadcasters aiming for ultra-low latency without compromising quality. Its built-in ABR encoding ensures smooth playback across varying network conditions.
Ant Media Server
Ant Media Server is another powerful solution that integrates adaptive bitrate streaming with support for multi-bitrate live video streaming. Recognized for its low-latency performance, this solution provides ABR technology that dynamically adjusts stream quality based on real-time network conditions. With broad compatibility across RTMP adaptive bitrate, WebRTC, and HLS, it serves businesses and developers seeking a scalable, flexible streaming infrastructure.
AI-Powered Enhancements in ABR
There is always a high demand for high-quality video streaming, which is why adaptive bitrate streaming technologies are essential in delivering smooth and uninterrupted viewing experiences. However, the future of ABR is now being shaped by the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) to enhance streaming quality and efficiency. AI-powered enhancements in ABR to improve video quality, reduce buffering, and optimize bandwidth usage.
AI-Based Optimization
AI uses machine learning algorithms to analyze real-time network conditions, user behavior, and device capabilities to adjust streaming quality dynamically. These algorithms continuously assess available bandwidth and latency to avoid buffering or interruptions.
AI-powered ABR technology enables streaming services to offer smoother playback, even under fluctuating network conditions. This means automatically selecting the most appropriate video bitrate and resolution and a seamless user experience without the need for manual intervention.
Context-Aware Encoding
Context-aware encoding is an advanced AI-driven technique that takes into account scene complexity to optimize video quality and bitrate in real time. Instead of encoding a video at a uniform quality throughout, AI algorithms adjust the video stream based on factors such as motion, detail, and content type.
For example, in a static scene, the encoder may reduce the bitrate without compromising quality. On the other hand, a fast-moving scene may require a higher bitrate for optimal clarity. This technique minimizes storage requirements and bandwidth usage while maintaining high video quality. It’s especially true on devices with limited resources or in environments with poor network connectivity. It ensures that the ABR streaming process is not just efficient but also tailored to the content being delivered.
Semantic-Aware Streaming
One of the most cutting-edge AI advancements in ABR technology is the use of latent diffusion models in semantic-aware streaming. These AI models can compress video content into latent spaces while preserving key visual and semantic information. It allows for high-quality streaming with minimal bandwidth consumption.
Focusing on the most important parts of a video, such as faces or key objects, allows these models to significantly reduce the need for excessive data usage, especially in complex scenes. Semantic-aware streaming enhances video quality without overloading the network. It’s the reason why it’s an ideal solution for both live streaming and video-on-demand services where bandwidth efficiency is critical.
This technology is at the forefront of video streaming, offering a new level of optimization that balances performance and quality.
Future Trends and Considerations
As we look to the future, several key trends will shape the next generation of ABR. These innovations are expected to improve video delivery, reduce latency, and enhance the quality of experience for users across the globe.
Join us as we highlight how these developments will impact ABR streaming, empower content creators, and provide viewers with faster, more reliable, and higher-quality video experiences.
5G and Beyond
The rollout of 5G networks and the upcoming development of post-5G technologies will have a profound impact on adaptive bitrate streaming. 5G promises to deliver higher bandwidth, lower latency, and more reliable connections compared to current 4G technologies, enabling smoother ABR experiences. With 5G, streaming services will be able to deliver higher-quality video, including 4K and even 8K content, to more users simultaneously, even in densely populated areas.
The increased stability and speed of 5G networks will minimize buffering and allow for more efficient adaptive media delivery. This will contribute to better streaming for mobile devices, remote areas, and environments with fluctuating network conditions. As the global shift toward 5G continues, ABR technology will evolve to harness its full potential.
Edge Computing Integration
Edge computing is set to become a key player in enhancing ABR performance. The processing of data closer to the end-user means that edge computing reduces the time it takes to deliver content. At the same time, it minimizes latency and improves content delivery efficiency. For ABR streaming, this means faster switching between different bitrates, improved responsiveness to changing network conditions, and reduced buffering.
Streaming platforms can use edge servers to store video content in locations closer to viewers, ensuring faster load times and smoother playback. This is particularly beneficial for large-scale events, such as live sports broadcasts, where low latency and uninterrupted streaming are critical. By combining ABR technology with edge computing, streaming providers can offer a more efficient, responsive, and scalable solution for global audiences.
FAQ
1. What is Adaptive Bitrate Streaming (ABR), and why is it important?
ABR is a technology that dynamically adjusts video quality in real-time, based on the viewer’s internet speed and device capabilities. This ensures a smooth, uninterrupted viewing experience by reducing buffering and optimizing video quality. ABR is essential because it improves user experience, increases viewer retention, and ensures consistent content delivery across different devices and varying network conditions, ultimately enhancing the overall quality of streaming.
2. How does ABR differ from Multi-Bitrate (MBR) streaming?
ABR and MBR both involve multiple video quality options, but they differ in how the quality is selected. ABR automatically adjusts the video stream in real time based on the viewer’s current network conditions and device performance, ensuring a seamless experience with minimal buffering. In contrast, MBR allows viewers to manually select from a range of quality options, but it does not adjust automatically when network conditions change, which can lead to buffering if the selected bitrate exceeds the available bandwidth.
3. What is an ABR ladder, and how does it improve streaming quality?
An ABR ladder is a set of video streams encoded at different bitrates and resolutions, which the video player can switch between based on real-time network speed and device capabilities. By offering a variety of stream options, the ABR ladder ensures that viewers always experience the best possible video quality for their available bandwidth, eliminating interruptions and buffering. This dynamic adjustment guarantees smooth playback, regardless of fluctuating internet speeds.
4. What are the best bitrates for adaptive streaming?
The ideal bitrates for adaptive streaming depend on the target resolution and the viewer’s network conditions. Here are some general recommendations for common resolutions:
- 360p: 400 Kbps – 1 Mbps
- 480p: 500 Kbps – 2 Mbps
- 720p: 1.5 Mbps – 4 Mbps
- 1080p: 3 Mbps – 6 Mbps
By offering a range of bitrates, broadcasters ensure that users with varying bandwidth levels can access an optimal video experience, improving the overall streaming quality for all viewers.
5. Which streaming protocols support Adaptive Bitrate Streaming?
Popular streaming protocols that support ABR include:
- HLS (HTTP Live Streaming) The most widely used protocol for ABR, compatible with most devices and browsers.
- DASH (Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP): A codec-agnostic protocol used for adaptive streaming, supported on modern devices.
- RTMP (Real-Time Messaging Protocol): Often used for video ingestion before transcoding into ABR-friendly formats like HLS or DASH.
6. How can I implement Adaptive Bitrate Streaming for my broadcasts?
To implement ABR streaming for your broadcasts:
- Transcode your content into multiple bitrates using a suitable video encoder.
- Segment your video files into smaller chunks (typically 2-10 seconds) to allow for seamless bitrate switching.
- Generate manifest files (M3U8 for HLS, MPD for DASH) that guide the video player on which stream to choose.
- Deploy a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to optimise global video distribution, reducing latency and buffering.
- Use an adaptive video player (such as an HTML5-based player) that supports ABR to adjust quality based on network conditions automatically.
Conclusion
Broadcasters need to prioritize their user experience, and ABR live streaming is a surefire way for users to view the highest quality stream possible on nearly any device. ABR streaming has created new user expectations that require the right streaming technology to meet.
As a comprehensive over-the-top (OTT) streaming platform, Dacast makes it straightforward to deliver adaptive bitrate streams with its flexible video ABR encoding capabilities and HTML5 adaptive video player. That’s why the streaming platform was nominated as the best platform for Small/Medium businesses in the 2019 Streaming Media Readers’ Choice Awards. Dacast was also listed as one of the Most Important Companies in Online Video Tech.
You can try Dacast and all its features today with our 14-day free trial.
Find out how easy it is to set up and manage adaptive bitrate streams using the OTT platform. For exclusive offers and live streaming tips, you can join our LinkedIn group.
 Stream
Stream Connect
Connect Manage
Manage Measure
Measure Events
Events Business
Business Organizations
Organizations Entertainment and Media
Entertainment and Media API
API Tools
Tools Learning Center
Learning Center Support
Support Support Articles
Support Articles